Allergic Skin
When the skin sounds the alarm
Allergic skin reactions
Development, causes, symptoms
Redness, itching, blisters - when the skin sounds the alarm, an allergy may be the cause. This is an overreaction of the immune system to substances that are normally harmless to humans. Among the triggers (allergens) are proteins in food, medications or insect venoms. But proteins on pollen or UV rays can also leave unpleasant marks on the skin.
Allergy symptoms of the skin include: Itching, reddened, dry skin areas, wheals and sometimes slight swelling or flaking.
Allergy types
Allergic skin reactions can be very different and are therefore divided into four different categories. The two best known are the immediate and delayed type allergies:
- Occurrence: Within seconds or minutes, but symptoms may subside just as quickly.
- Other symptoms: Often associated with runny nose, watery eyes, etc.
- Triggers: Pollen, house dust mites, animal hair etc.
- Origin: After a first contact with the trigger, the body forms an antibody subtype (IgE antibody). On second contact (sometimes even later), this IgE antibody causes an allergic reaction.
- Occurrence: Within hours or up to two days, can in principle occur all over the entire body.
- Triggers: Nickel, latex or fragrances and preservatives in cosmetics, among others.
- Origin: Develops after a so-called sensitisation phase, which can last for years and in which initially no skin reactions occur. If the allergens enter the body after repeated contact, T-lymphocytes and helper cells attack them directly. In the course of eliminating the allergen, they cause the allergic reaction.

Pollen allergy
Allergic skin reactions caused by pollen from grass, shrubs etc.
It begins with hazel in December and ends with grass in October: The pollen season makes the noses of pollen allergy sufferers run and the eyes water.
Hay fever is one of the most widespread allergies. Pollen allergy belongs to the immediate type, for the symptoms appear within a very short time after contact with the allergens. They not only appear on the mucous membranes of the eyes and nose, The skin of allergy sufferers also reacts to the pollen. The following applies here: The drier the skin - i.e. the more damaged the skin barrier - the more difficult it is for it to fulfil its protective function. Once the pollen has penetrated the skin, the immune system is activated and the skin shows an allergic reaction through itching or redness.
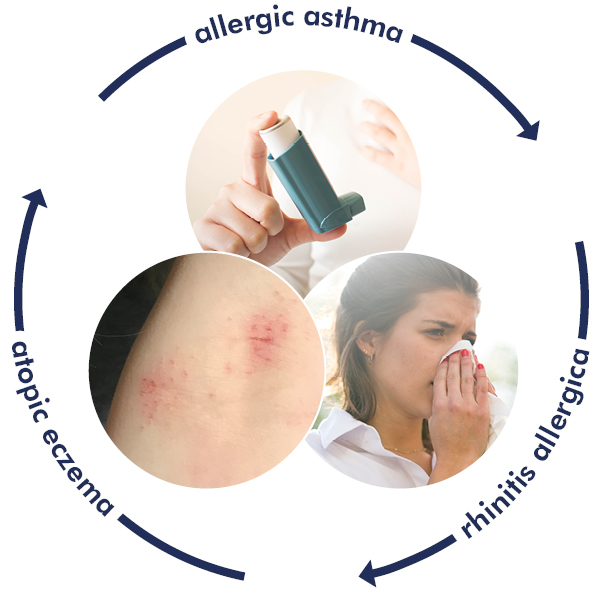
Neurodermatitis sufferers have a greater tendency to such symptoms due to their weakened skin barrier. In addition to neurodermatitis (atopic eczema), hay fever or allergic rhinitis (rhinitis allergica) often occurs in combination with allergic asthma. In medication, this triple constellation is referred to as the "Atopic disorders".
Care tips during pollen season
Medicinal skin care can protect the skin both through preventative care and acute care during the pollen season. The most important objectives: Reduce discomfort and support the damaged skin barrier! A resistant skin barrier offers the best protection against the penetration of pollen and other allergens. It thus effectively reduces the tendency to allergic skin reactions.
- DERMASENCE Vitop forte Eye care – soothes irritated eye areas and provides valuable moisture
- DERMASENCE Polaneth Lotion – immediately relieves itching and other discomforts
- DERMASENCE BarrioPro Barrier-building facial emulsion – regenerates irritated facial skin prone to redness

Itchy skin after sunbathing
Red, itchy skin changes that occur after contact with the sun's rays are often colloquially called a "sun allergy". However, this term is usually inappropriate. In fact, they are usually so-called light dermatoses (also photodermatoses), i.e. skin changes caused by sunlight.
They occur on the so-called skin "sun terraces" (décolleté, shoulders, neck, face, hands).
In contrast to sunburn, where there is excessive contact with UV-B radiation, in cases of photodermatoses it is UV-A radiation that plays the more significant role. Important: UV-A rays are not blocked by window panes. Therefore, symptoms of "sun allergy" can also occur in cars or in rooms with glazing.
Most frequent form of skin changes caused by sunlight (10-20% of Central European people are affected)
- Affected: Predominantly children and young women with a fair skin type
- Symptoms: Very itchy, blotchy rashes, wheals and vesicles
- Occurrence: Within a few hours or days after sunbathing
- Cause: Not yet conclusively clarified
Special form of PLD, also called "acne aestivalis" or "summer acne".
- Affected: Predominantly young women
- Symptoms: Similar to acne, papules and pustules form. In addition, wheals and severe itching may occur
- Occurrence: Within a few hours after sunbathing
- Cause: Intolerance to the combination of sunlight and emulsifiers/ certain fats from skin care causes inflammation of the sebaceous follicles.
Increased sensitivity to light (photosensitisation) due to selected substances
- Symptoms: Burning, redness, possibly blisters (similar to sunburn)
- Occurrence: Within a few hours after sunbathing (even after comparatively short contact with the sun).
- Cause: The combination of sunlight and a certain photosensitising substance in or on the body causes immunologically induced damage to the skin cells. Possible substances include medications (e.g. antibiotics), cosmetic substances (e.g. perfume) and chemicals (e.g. cleaning agents).
The only "real" allergic skin reaction that occurs only rarely and is a special form of contact dermatitis.
- Symptoms: Severe itching, redness, blisters.
- Occurrence: After several hours to days after sunbathing
- Cause: As is usual for contact dermatitis, the skin reacts to selected substances (especially medications, more rarely also UV filters) only after a sensitisation phase. In photoallergic contact dermatitis, the skin reactions occur after contact with the respective substance and sun exposure. The immune system is also involved in the phototoxic reaction.
Care tips for sunny days
Skin Care products with broadband protection that protect the skin from UV-B and UV-A rays are especially important for people prone to light dermatoses. DERMASENCE Solvinea Sun protection gel cream SPF 50+ is ideal for sensitive skin and, due to its oil- and fragrance-free formulation, is also suitable for those with a tendency to "Mallorca acne".
After sunbathing, we recommend the DERMASENCE Aloe Vera Active Gel for cooling and moisturising care. For acute skin changes, the DERMASENCE Seborra Zinc repair foam soothes and calms irritations.

Cosmetic substances as allergy triggers
If unpleasant skin changes such as burning, itching or redness occur after applying cosmetics, an allergic reaction may exist. As a rule, this is a case of a contact allergy (late type IV) whose symptoms sometimes only appear days after the contact. Fragrances (e.g. citronellol or geraniol) and preservatives are the main focus of allergies caused by cosmetics.
In order to make it easier for allergy sufferers to check the constituents of creams, lotions and other cosmetics, every product package provides a list of the substances it contains, the so-called INCI (International Nomenclature of Cosmetic Substances ). Please note, however, that the INCI designation may differ from those in allergy passports. It is therefore advisable to discuss this with your doctor or allergist.
Not all perfuming substances have to be listed individually in the INCI. This only applies to the 26 fragrances that most frequently cause allergies in people in Europe. A list of these fragrances that must be declared can be found on the website of the Federal Office of Consumer Protection and Food Safety. All other fragrances may be grouped under the term "perfume".
Fragrances at DERMASENCE: All DERMASENCE products do not contain any fragrances or fragrance mixtures that have to be declared. In addition, the number of completely fragrance-free skin care products is growing continuously. You will find a complete product list in our FAQs.
The Cosmetics Ordinance determines which preservatives may be used in cosmetics after thorough testing and examination.
Fact is: Without preservative substances (e.g. parabens), skin care products would spoil faster. This in turn can increase the risk of allergies and skin diseases. Consequently, preservatives help to protect against allergies in many cases.
Preservatives at DERMASENCE: We use high-quality dispensers that minimise contamination with oxygen and germs. This allows us to keep the amount of preservatives in products low.
Natural plant extracts are often used in natural cosmetics (e.g. essential oils). In addition to the effective part of the extract, these also contain substances that can cause intolerances and allergies.
Plant power at DERMASENCE: In order to be able to guarantee a particularly high skin compatibility, we use purified substances wherever possible. These have undergone a chemical process in which the allergenic components have been removed from them. You can find out more about this on our "Effectiveness Concept".
Care tips for particularly sensitive skin
Since allergies cannot be cured, the only option for those affected is to avoid the allergy-causing substances. We also recommend the following tips:
- Try new skin care products as rarely as possible. Whenever possible, stick to tried and tested products that you tolerate well.
- Always check the INCI even when repurchasing known products. Most manufacturers occasionally make changes to substances to optimise their skincare products.
- When using a new product, look for a short INCI and/or medicinal skin care product with a high skin tolerance.
- Test new cosmetics on your forearm for a few days first. You can obtain suitable product samples for this purpose from your pharmacy.
Skin tolerance is one of DERMASENCE's most important goals, along with effectiveness. To ensure that people with sensitive skin can also use our skin care products without hesitation, we use purified, highly compatible substances and do not use any fragrances that have to be declared.